The Essential Building Blocks: Macromolecules and Micromolecules in Your Daily Diet
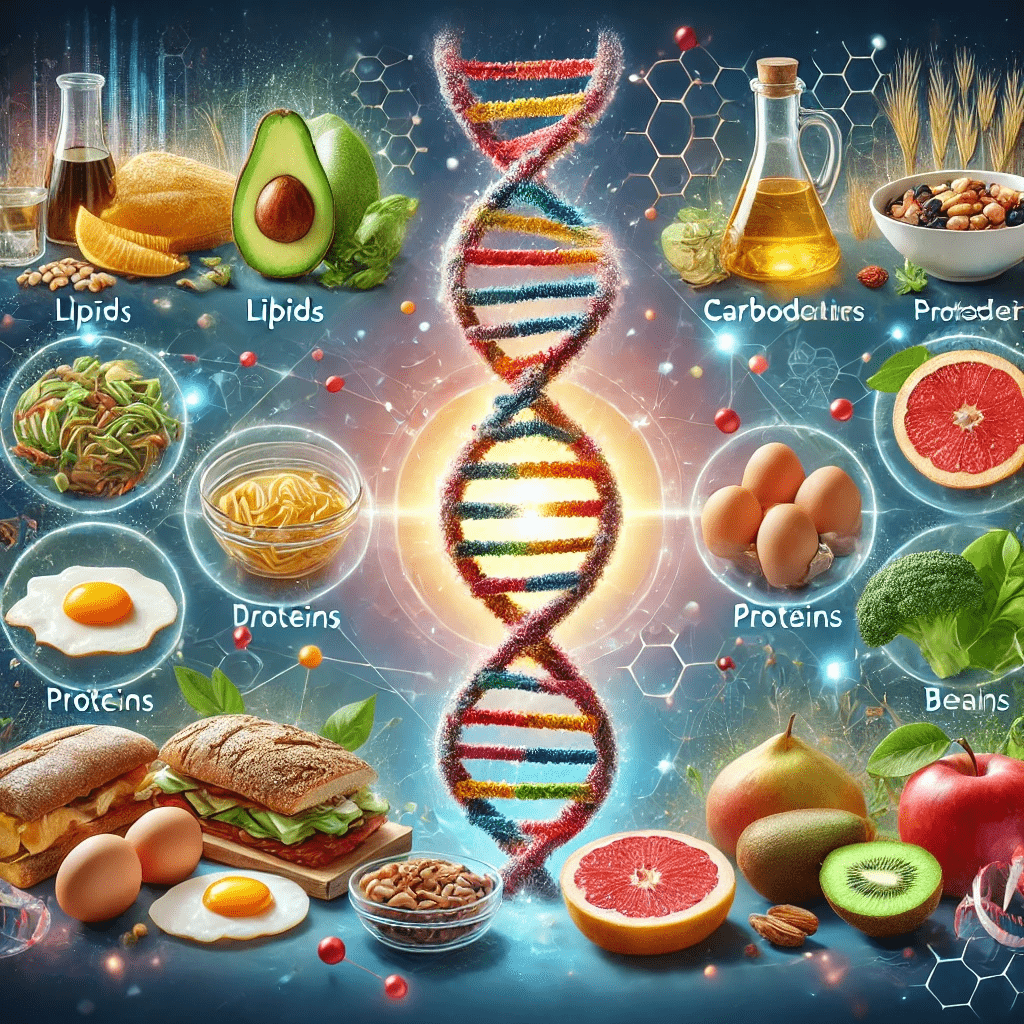
In our quest for a healthy lifestyle, it is crucial to understand the significance of macromolecules and micromolecules in our diet. These molecules are the fundamental building blocks of life, playing vital roles in various biological processes. In this article, we will explore the definition of macromolecules and micromolecules, highlight their benefits, and emphasize the importance of including them in our daily diet.
Understanding Macromolecules: Macromolecules are large, complex structures made up of smaller units known as monomers. There are four primary types of macromolecules found in our diet: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids (fats), and nucleic acids. Each type of macromolecule serves a unique purpose in our bodies.
1.Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for our bodies. They are composed of sugar molecules, such as glucose and fructose, and can be found in various forms such as starches, fibers, and sugars. Carbohydrates provide energy, support brain function, aid in digestion, and assist in maintaining a healthy weight.\r\n2.Proteins: Proteins are crucial for the growth, repair, and maintenance of our body tissues. They are composed of amino acids, which act as the building blocks of proteins. Proteins play a vital role in muscle development, immune system function, enzyme production, and hormone regulation. Including adequate protein in our diet promotes healthy bones, skin, and hair.\r\n3.Lipids (Fats): Lipids, commonly known as fats, are essential for our body’s overall health. While they are often associated with weight gain, healthy fats are actually crucial for proper brain function, vitamin absorption, hormone production, and insulation of vital organs. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, found in foods like avocados, nuts, and oily fish, are considered healthy fats that support cardiovascular health.\r\n4. Nucleic Acids: Nucleic acids are involved in the storage and transmission of genetic information. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are two types of nucleic acids found in our cells. They play a fundamental role in cellular processes, genetic expression, and protein synthesis. Consuming a balanced diet that includes nucleic acids supports optimal cellular function and overall health.\r\nExploring Micromolecules: Micromolecules, also referred to as micronutrients, are substances required by our bodies in smaller quantities. They include vitamins and minerals, which are essential for various physiological functions.\r\n\r\nVitamins: Vitamins are organic compounds that help regulate bodily functions, support growth, and provide antioxidant protection. There are two categories of vitamins: fat-soluble (A, D, E, and K) and water-soluble (B vitamins and vitamin C). A well-rounded diet incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins ensures an adequate intake of vitamins.\r\nMinerals: Minerals are inorganic substances that play crucial roles in maintaining healthy bones, regulating fluid balance, supporting nerve function, and aiding in muscle contractions. Examples of essential minerals include calcium, iron, potassium, and zinc. These minerals can be obtained through a diverse diet that includes foods like dairy products, leafy greens, legumes, and lean meats.\r\nThe Importance of Macromolecules and Micromolecules in Your Daily Diet: Including both macromolecules and micromolecules in your daily diet is essential for overall health and well-being. These molecules work synergistically to provide energy, support growth and repair, enhance immune function, and maintain vital bodily functions. A well-balanced diet that includes carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals.