How to calculate your daily required calorie intake like a professional Dietitian.
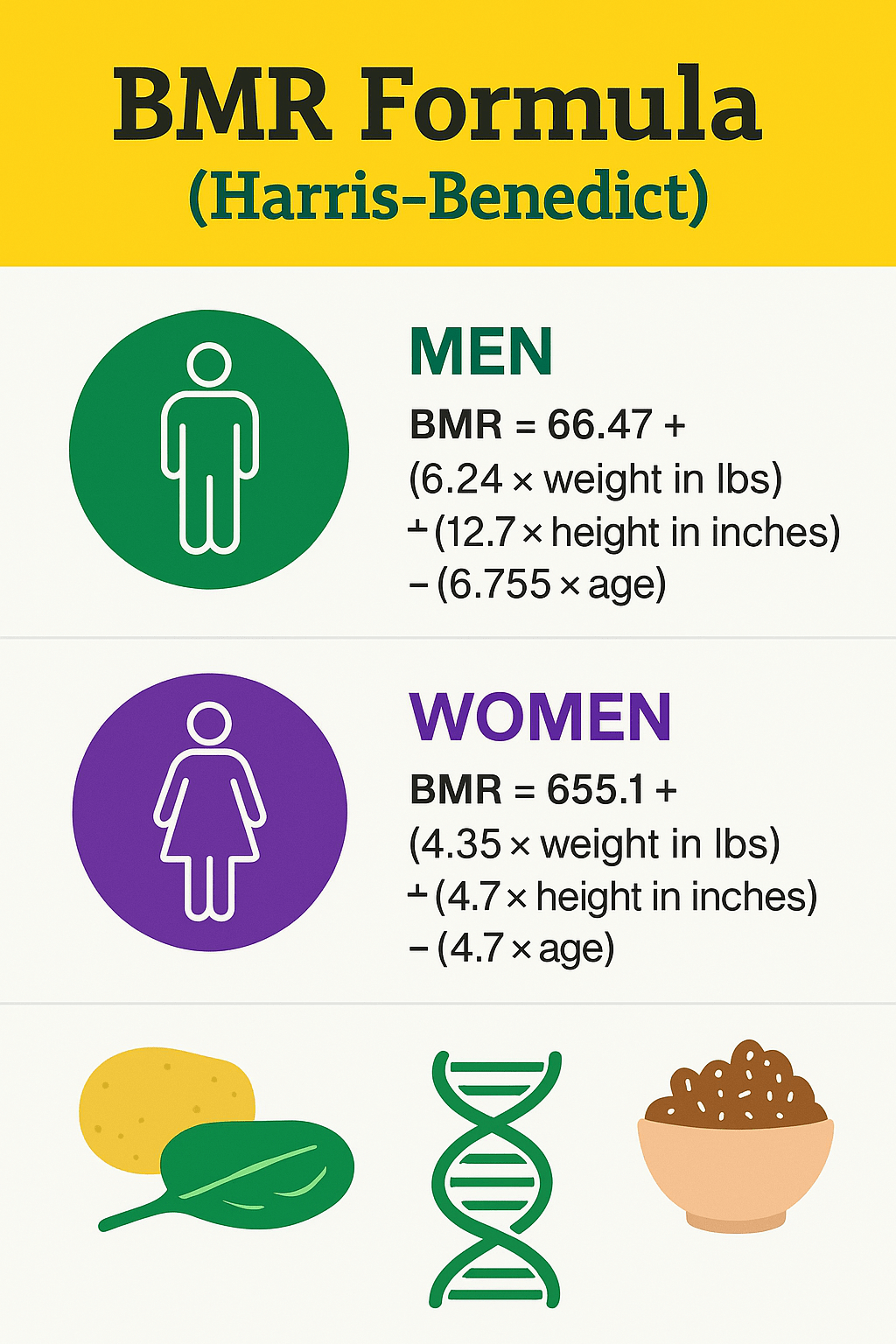
Basal Energy Expenditure (BEE), also known as Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR), represents the number of calories your body needs to maintain basic physiological functions at rest. These functions include breathing, circulating blood, regulating body temperature, and supporting organ function. Calculating your BEE is important as it serves as the foundation for determining your total daily energy expenditure and can be helpful in managing weight, planning diets, or creating exercise plans.
The Harris-Benedict equation is a widely used formula for estimating BEE. It takes into account factors such as age, sex, height, and weight to provide a rough estimate of the number of calories your body needs in a day.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Basal Energy Expenditure using the Harris-Benedict Equation:
Step 1: Determine your sex (male or female).
Step 2: Measure your weight in kilograms (kg). If you know your weight in pounds (lbs), you can convert it to kilograms by dividing the weight in pounds by 2.205.
Step 3: Measure your height in centimeters (cm). If you know your height in feet and inches, you can convert it to centimeters by multiplying the feet by 30.48 and adding the inches multiplied by 2.54.
4: Determine your age in years.
Step 5: Use the appropriate formula based on your sex:
For males: BEE = 88.362 + (13.397 x weight in kg) + (4.799 x height in cm) — (5.677 x age in years)
For females: BEE = 447.593 + (9.247 x weight in kg) + (3.098 x height in cm) — (4.330 x age in years)
Step 6: Calculate your BEE using the formula based on your sex. This will provide an estimate of the number of calories your body needs to maintain basic functions at rest.
Note: The BEE calculated using the Harris-Benedict equation provides an estimate and is not an exact measurement. Individual variations, such as muscle mass, body composition, and metabolic health, can influence the actual BEE.
Additional Considerations: Physical activity level: The BEE calculated using the Harris-Benedict equation only accounts for your resting metabolic needs. To estimate your total daily energy expenditure, you need to consider your physical activity level. Multiply your BEE by an appropriate activity factor (e.g., sedentary: BEE x 1.2, lightly active: BEE x 1.375, moderately active: BEE x 1.55, very active: BEE x 1.725, extremely active: BEE x 1.9) Changes in weight and body composition: If you experience significant weight changes or alterations in body composition (e.g., muscle gain or loss), re-evaluating your BEE may be necessary to ensure accurate calorie intake. Remember, the Harris-Benedict equation is a useful tool for estimating BEE, but it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice and guidance regarding your nutritional needs and goals.